Pipeline
Microsurgical
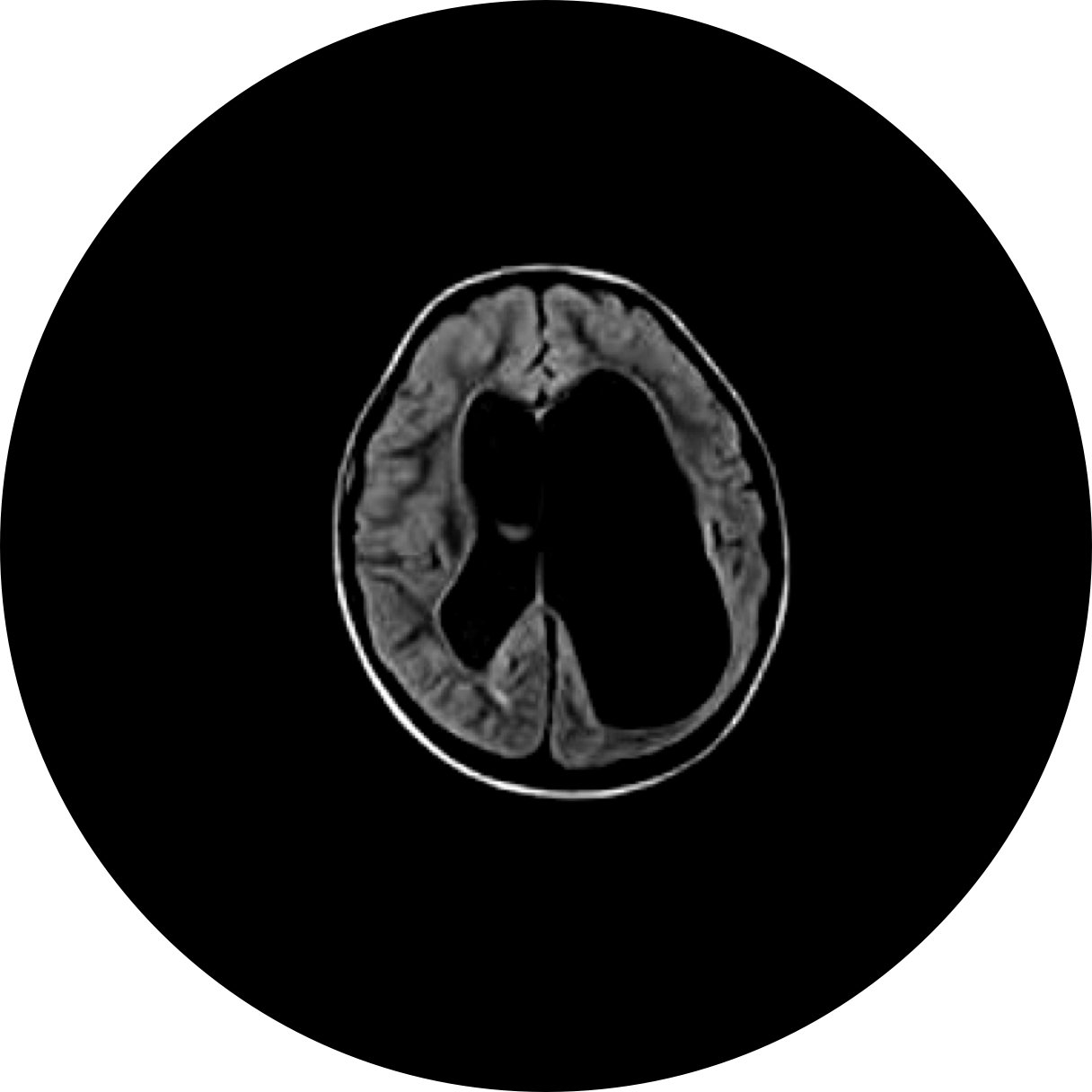
Hydrocephalus
An abnormal buildup of fluid in the ventricles (cavities) deep within the brain
Hydrocephalus is an abnormal buildup of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in the ventricles (cavities) within the brain. The extra fluid puts pressure on the brain and can cause brain damage. It is characterized by head enlargement in infants. Adults and older children experience headache, impaired vision, cognitive difficulties, loss of coordination, and incontinence.
Treatment options today often involve placing a tube (shunt) inserted surgically into a ventricle to drain excess fluid. These procedures are highly invasive and are a source of serious complications leading to suboptimal outcomes requiring life-long monitoring and the need for additional surgical interventions.
The Bionaut approach to addressing hydrocephalus
Provide a safe, minimally invasive alternative to current treatment options of shunting and endoscopic third ventriculostomy (ETV) using an externally powered and remotely guided microsurgical robot designed to treat obstructions in normal cerebrospinal fluid circulation.
Minimize the risks of complications arising from conventional surgical procedures and shunt infections by offering a minimally invasive protocol.
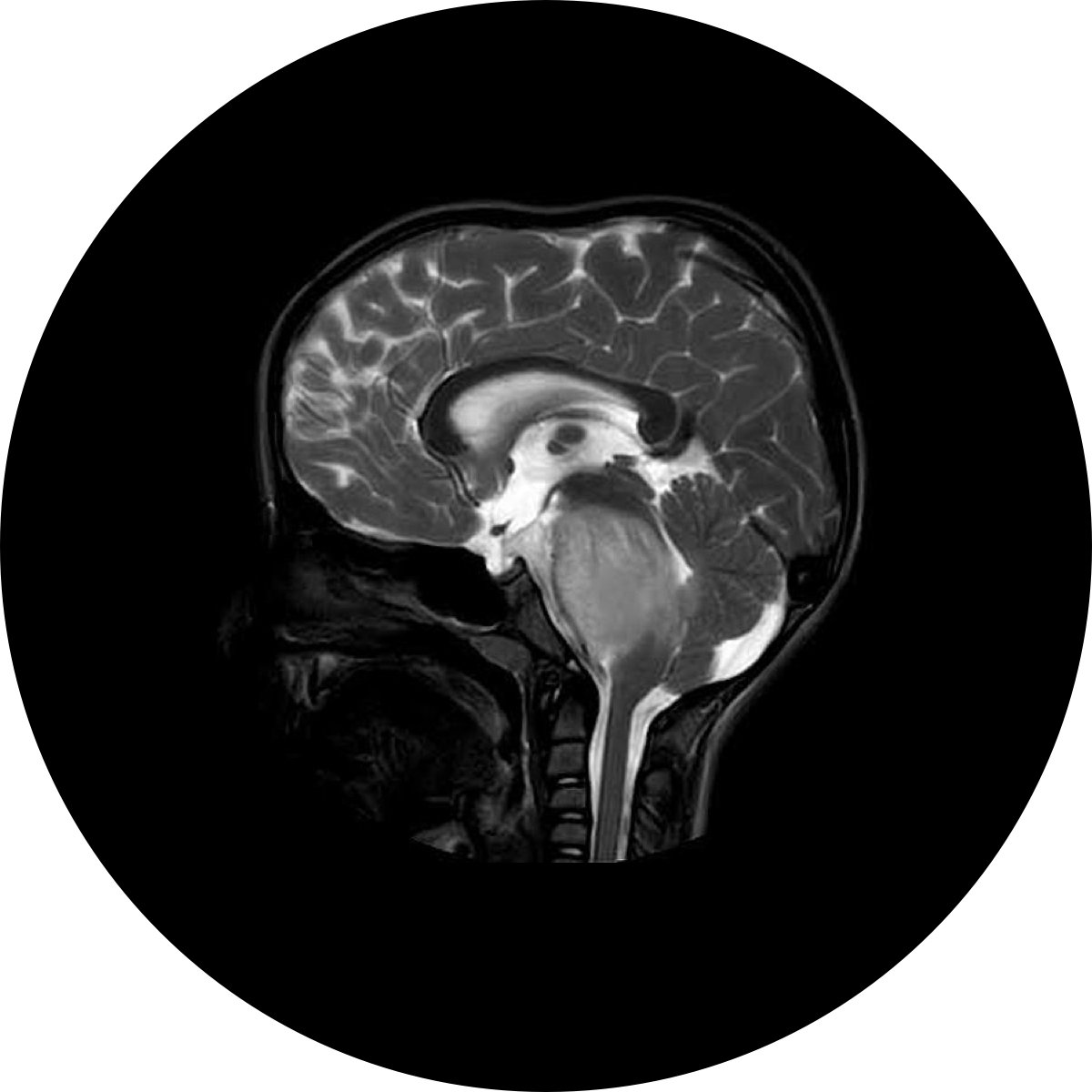
Dandy Walker Malformation
A clinical syndrome manifesting as the congenital constellation of a posterior fossa cyst, hypoplasia of the cerebellar vermis, and obstructive hydrocephalus.
Condition: A congenital condition manifesting in an obstructive hydrocephalus cyst in which blockage of the normal CSF flow leads to excessive amounts of fluid accumulating in and around the brain. This results in abnormally high pressure within the skull and swelling of the head, which can cause neurological impairment.
Incidence: A rare condition affecting 1 in 25,000–30,000 births in the U.S.
Standard of care/limitations: Current treatments of DWM include shunting of the CSF ventricular system and endoscopic third ventriculostomy. These invasive procedures necessitate the need for revisions or additional surgical interventions, and carry risks of severe complications leading to suboptimal clinical outcomes, including wound healing issues, surgical infections, and concerns for acquisition of additional neurological deficits.
The Bionaut approach: The DWM Bionaut™ is designed to safely reach targets in the lower occipital section of the brain via minimally invasive microsurgery to directly fenestrate the hydrocephalus cyst for therapeutic CSF diversions as an alternative to highly complex posterior craniotomy or shunts.
Stage: Pre-clinical (FDA Humanitarian Use Device designation granted in 2021)
Therapeutic
Neuro-oncology
Tumors of the nervous system
Brain tumors are the second leading cause of cancer death in children under age 15 and the second fastest growing cause of cancer death among those over age 65. Over the next year, more than 100,000 people in the United States will be diagnosed with a brain tumor.
Despite aggressive surgical and adjuvant therapeutic strategies, treatment of both pediatric and adult brainstem tumors remains problematic. While novel strategies to enhance drug exposure in brain cancers have been proposed, the field is still in need of treatments that exhibits dramatically enhanced potency with optimal therapeutic outcome.
The Bionaut Approach to treating Brain Tumors
A platform to provide localized treatment of neoplasias that can be combined with conventional systemic and radiotherapy
Performing delivery and distribution in a precise and controllable fashion;
Automating and standardizing the process to reduce treatment variability
Maximizing the therapeutic outcome by increasing localized drug concentrations while reducing the overall systemic toxicity
Brainstem Glioma
Cancers formed in the tissues of the brain stem.
Condition: Brainstem tumors are defined as lesions occurring in the midbrain, the pons, or the medulla oblongata
Incidence: A rare condition with 300-400 pediatric cases diagnosed each year in the US
Standard of care/limitations: These tumors are inoperable and the effects of radiation therapy are temporary while no chemotherapeutic agent has demonstrated curative efficacy, leading to poor survival outcomes with median survival of 10 months post-diagnosis in pediatric patients
The Bionaut approach: Using the Bionaut to locally deliver a currently approved chemotherapeutic/radiosensitizing agent, doxorubicin, directly to the brainstem neoplasias to enhance the effect of conventional radiation therapy.
Stage: Pre-clinical (FDA ODD designation granted 2021)
Neurodegeneration
Progressive atrophy and loss of function of neurons such as Parkinson's and Huntington’s disease.
Neurodegenerative disorders encompass a wide range of conditions that result from progressive damage to cells and nervous system connections that are essential for mobility, coordination, strength, sensation, and cognition. Neurodegenerative diseases affect millions of people worldwide and is growing in prevalence in the aging global population.
While we’ve made significant strides in our understanding of neurodegenerative diseases in the last decade, unfortunately, effective therapies are lacking for the vast majority of conditions with progress hampered by inaccessibility of drugs into the deep centers of the brain.
The Bionaut Approach to treating Neurodegeneration
A safe, minimally invasive procedure to mediate localized treatment of difficult-to-reach, affected circuitry in the midbrain
Performing delivery and distribution of therapeutics in a precise and controllable fashion
Perform diagnostic procedures and monitor local therapeutic exposure or biomarkers with Bionaut technology
Automating and standardizing the process to reduce treatment variability from physician to physician
Maximizing the therapeutic outcome by increasing localized concentrations while reducing the overall systemic exposure to therapeutic agents